ROOT PUNCTURE RESISTANT WATERPROOF MEMBRANE
In today’s rapidly developing modern world, land resources in large and medium-sized cities have become “as precious as gold,” and the available area for greening is shrinking. Developing planted roofs and creating “sky gardens” has become an essential solution.
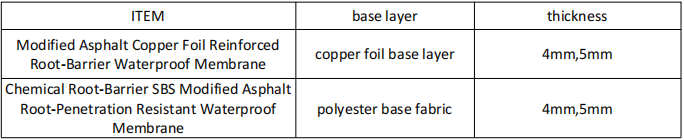
Modified Asphalt Copper Foil Reinforced Root-Barrier Waterproof Membrane: This is a top-layer waterproof material that prevents plant roots from penetrating. The base fabric is treated with copper vapor, which provides root-blocking effects without damaging the surrounding environment. Once plant roots come into contact with the copper base, they will automatically change direction and seek alternative paths to continue growing.
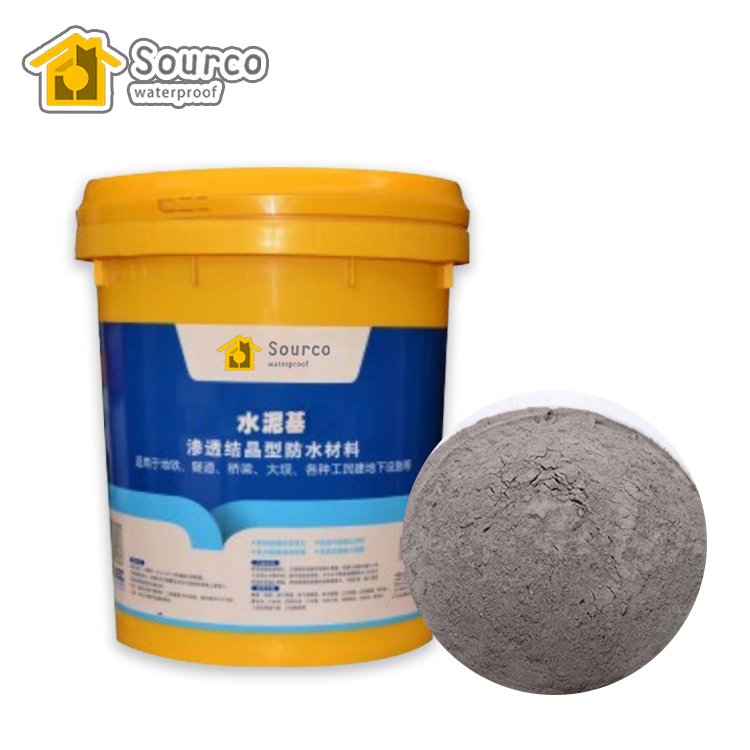
Chemical Root-Barrier Waterproof Membrane: This material is a combination of chemical root-inhibiting substances and modified asphalt, ensuring that plant roots, at a thickness of 20mm from the waterproof membrane, automatically change direction and continue growing, unable to penetrate the waterproof layer. It guarantees both the growth of plants and the waterproofing performance.
ROOT PUNCTURE RESISTANT WATERPROOF MEMBRANE DESCRIPTION
ROOF WATERPROOFING PUNCTURE RESISTANT MEMBRANE PRODUCT FEATURES
I Dual Function of Waterproofing and Root Penetration Prevention: This product can withstand root penetration while maintaining its waterproof function over time. It prevents root intrusion without affecting the normal growth of plants.
II High-Strength Waterproof Layer: Forms a robust waterproof barrier with excellent resistance to water pressure. It is also resistant to punctures, abrasion, tearing, and aging.
III High Tensile Strength: The modified asphalt coating layer is thick, offering strong adaptability to shrinkage, deformation, and cracking of the substrate.
IV Excellent Performance in Extreme Temperatures: It performs well in both high and low-temperature environments, making it suitable for use in cold or hot regions.
V Corrosion, Mold, and Weather Resistance: Highly resistant to corrosion, mold, and weathering.
VI Hot-Melt Application: Easy to apply with hot-melt methods, ensuring convenient installation and durable, reliable seams.
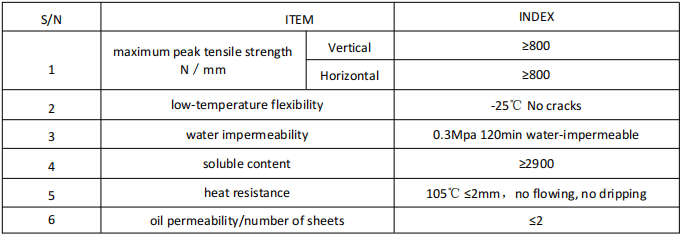
PERFORMANCE INDEX STANDARD JC/T1075-2008
ROOF WATERPROOFING PUNCTURE RESISTANT MEMBRANE PRODUCT CATEGORY
ROOF WATERPROOFING PUNCTURE RESISTANT MEMBRANE

 MAIN USE
MAIN USE
Places that urgently require both waterproofing and resistance to plant root growth, such as rooftop gardens, underground parking garage roofs, bridges, embankments, and similar structures.


CONSTRUCTION TECHNOLOGY
- Vegetation Layer: This layer consists of flowers, vegetables, medicinal plants, small shrubs, etc., planted in the soil.
- Planting Soil: The planting soil is the layer in which plants grow on the roof. It is divided into three types: agricultural soil, improved soil, and inorganic composite planting soil.
- Filter Layer: Located between the planting soil and drainage layer, this layer uses materials such as non-woven fabric or mineral wool mats with a weight of no less than 250g/m². Its function is to retain water and regulate excess water after rain or irrigation, ensuring that the excess water is filtered and drained away, preventing plant roots from rotting due to excess moisture. It also helps keep the planting soil in place and prevents its loss.
- Drainage Layer: The drainage layer uses embossed drainage boards, mesh interwoven drainage boards, or lightweight expanded clay with a particle size of less than 25mm. This layer serves to drain and store water.
- Root-Barrier Layer: To ensure that plant roots do not penetrate the roof, an additional root-resistant SBS-modified asphalt root-barrier waterproof membrane must be laid on top of the regular waterproof layer.
- Regular Waterproof Layer: In planted roof systems, in addition to using root-resistant waterproofing layers, a regular waterproofing membrane or coating should be applied beneath the root-barrier layer.
7. Slope Layer: To facilitate the rapid drainage of accumulated water on the planted roof and ensure proper plant growth, a sloping structure should be used to create an effective drainage slope.








